Atopic Dermatitis
Relieve and Manage Chronic Inflammatory Skin with Confidence
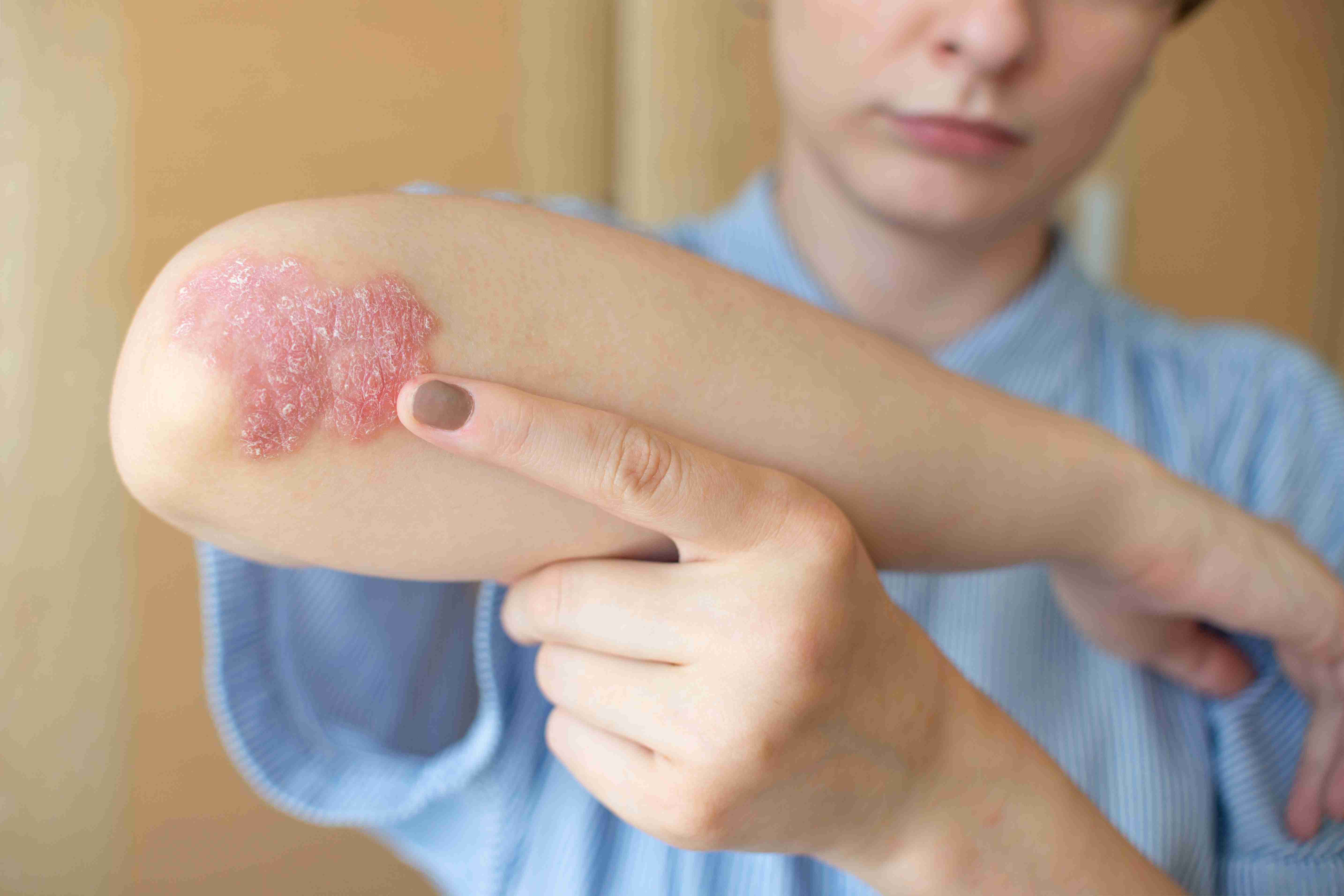
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing form of eczema that causes dry, itchy, inflamed skin. It often begins in childhood but can persist or start in adulthood. This condition is linked to an overactive immune response and a weakened skin barrier, making skin vulnerable to irritation, infection, and allergens. While not contagious, it requires ongoing care.
Treatment Options
Treatment Options for Acne

Laser Treatment
Advanced laser therapy for precise skin treatment and rejuvenation with minimal downtime and maximum results.
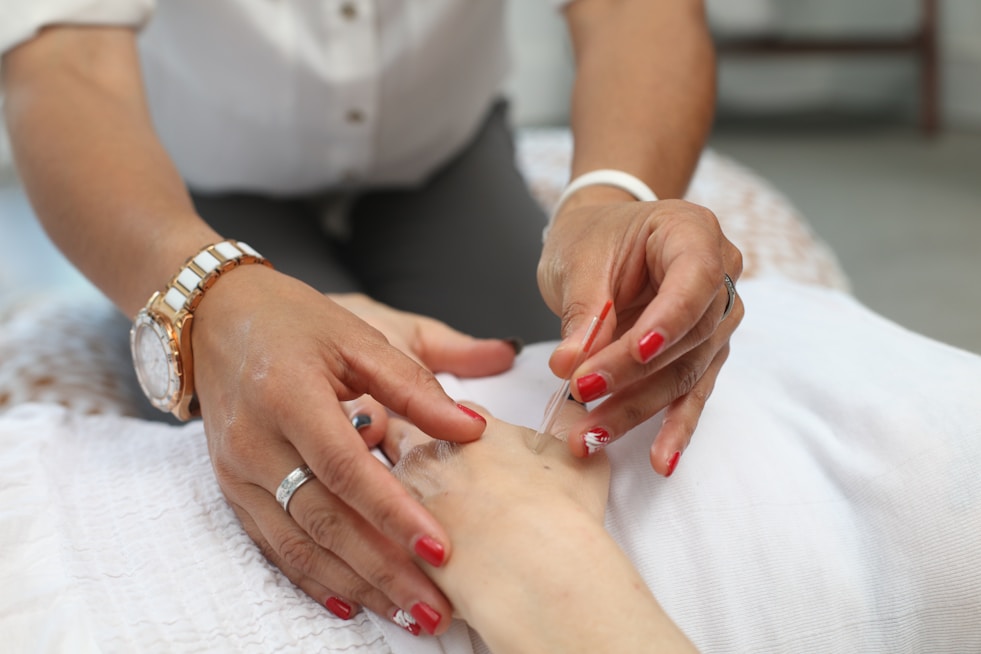
Chemical Peels
Professional chemical peel treatments to exfoliate and revitalize your skin for a fresh, youthful appearance.
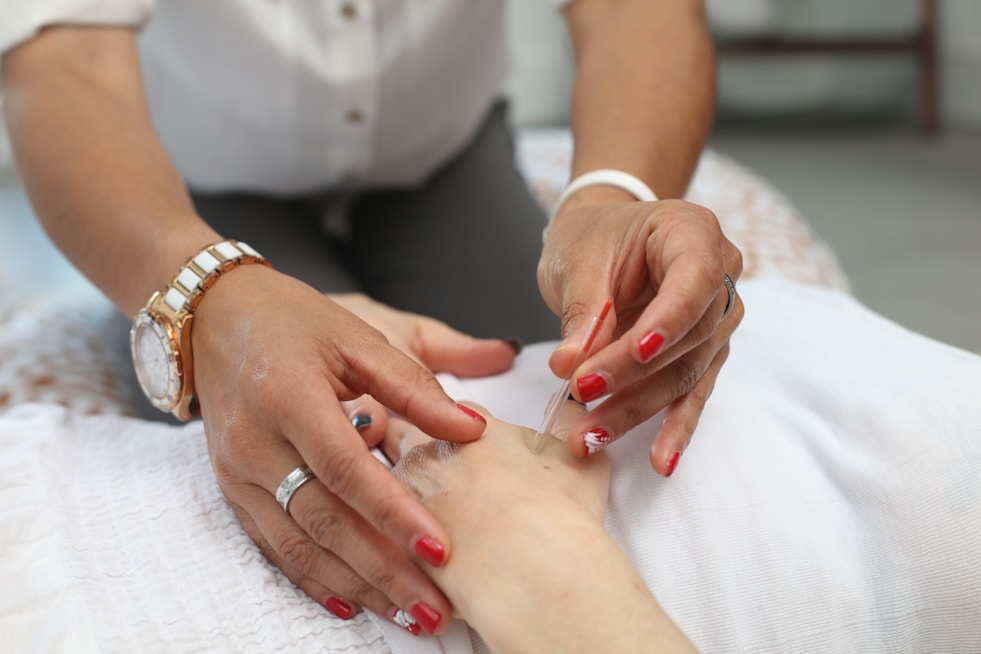

Topical Medications
Prescription-grade topical solutions customized for your specific skin condition and treatment needs.
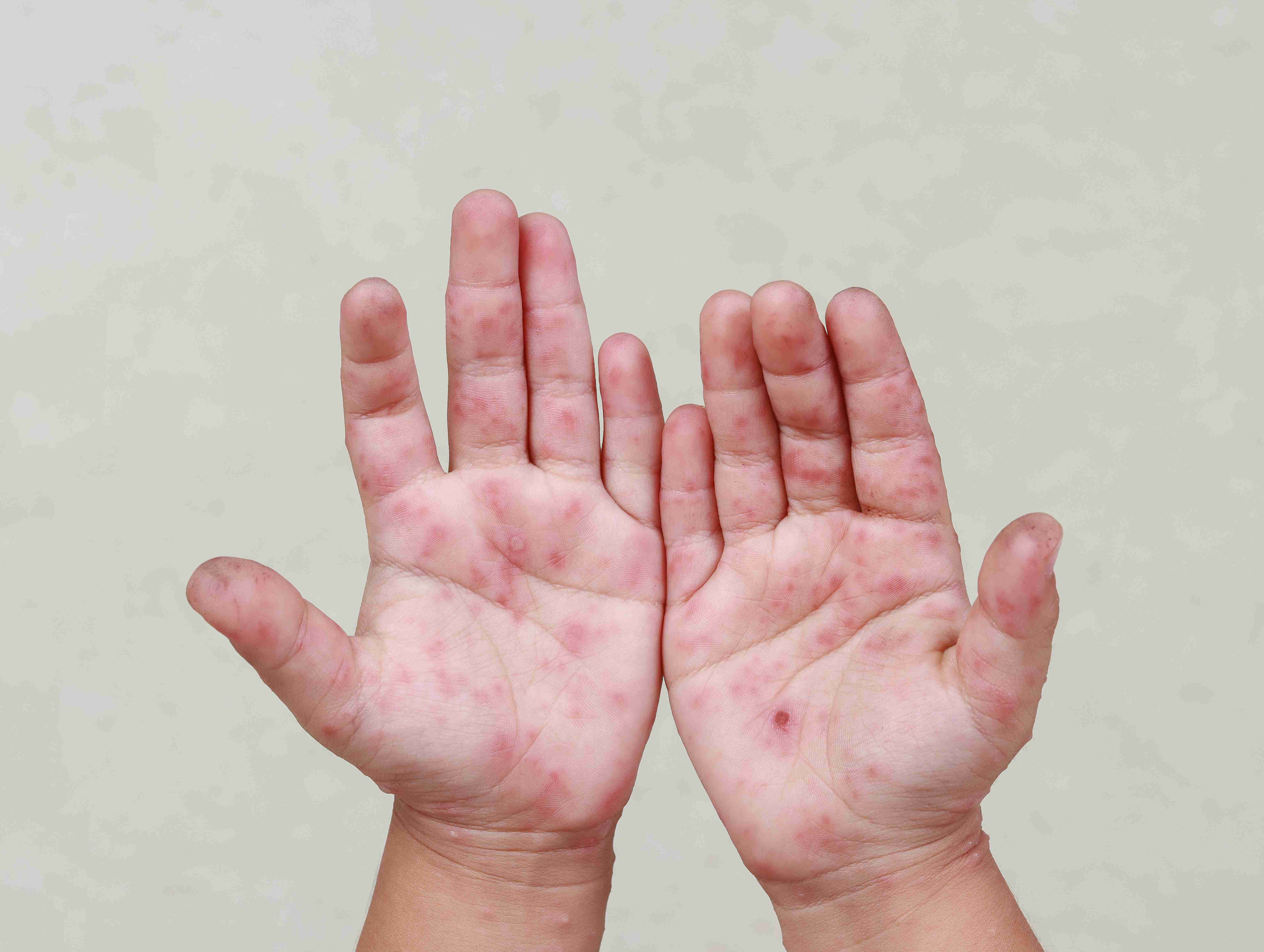
Who is at Risk?
Infants, children, and adults with a personal or family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis. It may begin in infancy and often improves with age, though it can persist or reoccur in adulthood.
Treatment Flow
01
Consultation & Skin Evaluation
Assessment of skin history, allergy tendencies, and current symptoms.
02
Prescription Regimen
Anti-inflammatory creams and moisturizers prescribed for short and long-term use.
03
Lifestyle & Trigger Guidance
Identify environmental, dietary, and clothing triggers and how to avoid them.
04
Monitoring & Flare Management
Regular follow-ups to adapt treatment and prevent flare-ups.
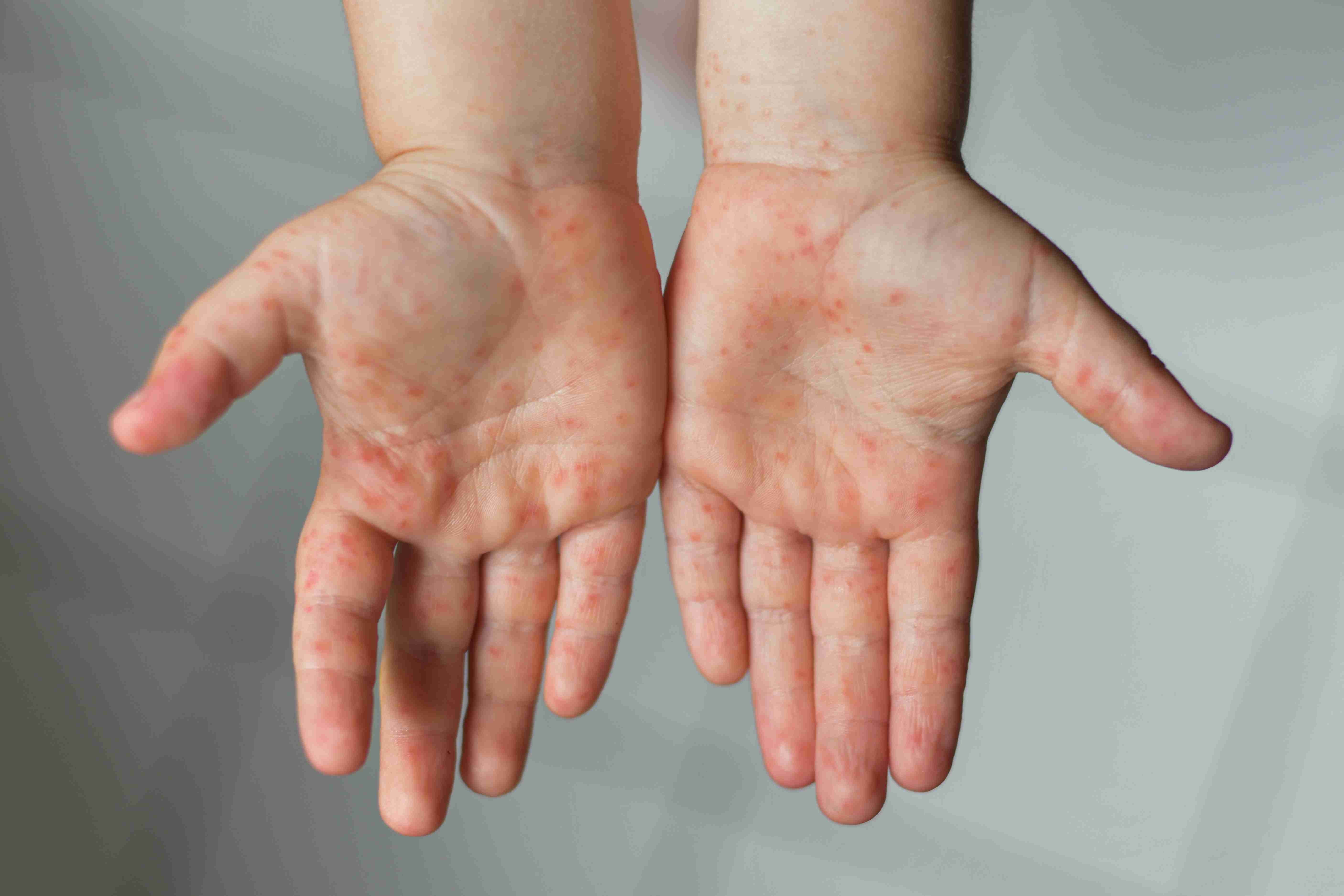
Results & Relief
Symptoms reduce within days of starting proper care.
Fewer flare-ups with long-term skin hydration and care.
Skin regains normal texture and tone over time.
Got Questions?We've Got Answers
Everything you need to know about donating, eligibility, and how The Blood App works. Can't find the answer you're looking for? Chat with our support team — we're here to help.
Atopic dermatitis is a type of eczema. All atopic dermatitis is eczema, but not all eczema is atopic.
Many children outgrow it by adolescence, but some may continue to have symptoms into adulthood.
In some individuals, certain foods (e.g., dairy, eggs) may trigger or worsen symptoms. Allergy testing may help.
There’s no permanent cure, but proper care and medication can control symptoms and prevent flares.
Yes, scratching can lead to skin breaks and secondary bacterial infections. Prompt treatment helps avoid this.
Start Your Personalized Skincare Plan
At ClairéDerma, we believe that healthy, radiant skinis the foundation of confidence and well-being. Ledby Dr. Mohna Chauhan, our clinic offers personalized dermatological care tailored to each patient's unique needs. With over a decade ofexperience and more than 3000 successfully treated patients,