Urticaria
Fast Relief from Itchy, Red Hives and Allergic Skin Reactions
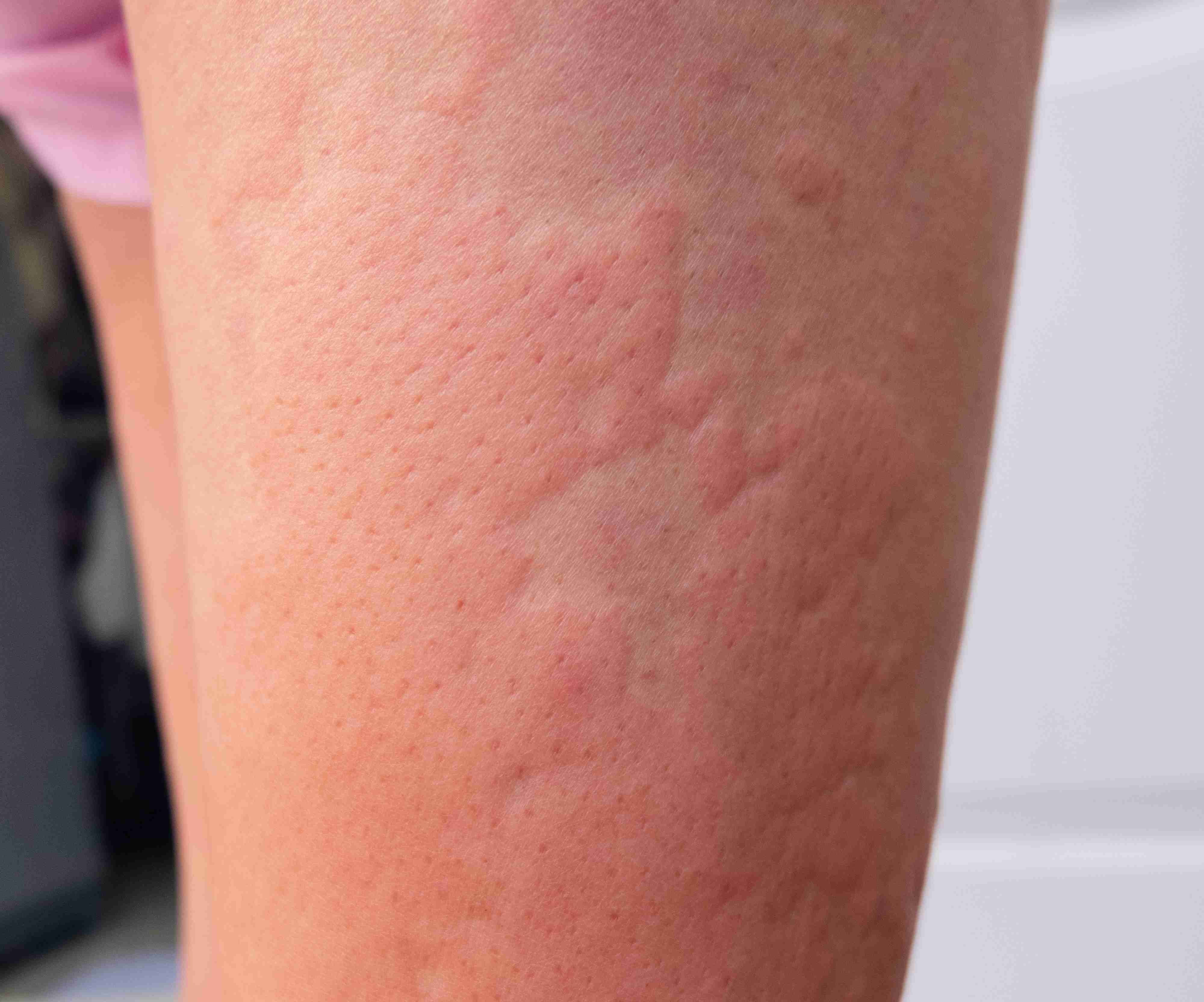
What is Urticaria?
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin reaction that causes red, raised, itchy welts or bumps on the skin. These can appear anywhere on the body and vary in size. Hives may last for a few hours or persist for days or weeks. While usually harmless, chronic urticaria can affect quality of life and may signal underlying allergies or autoimmune disorders.
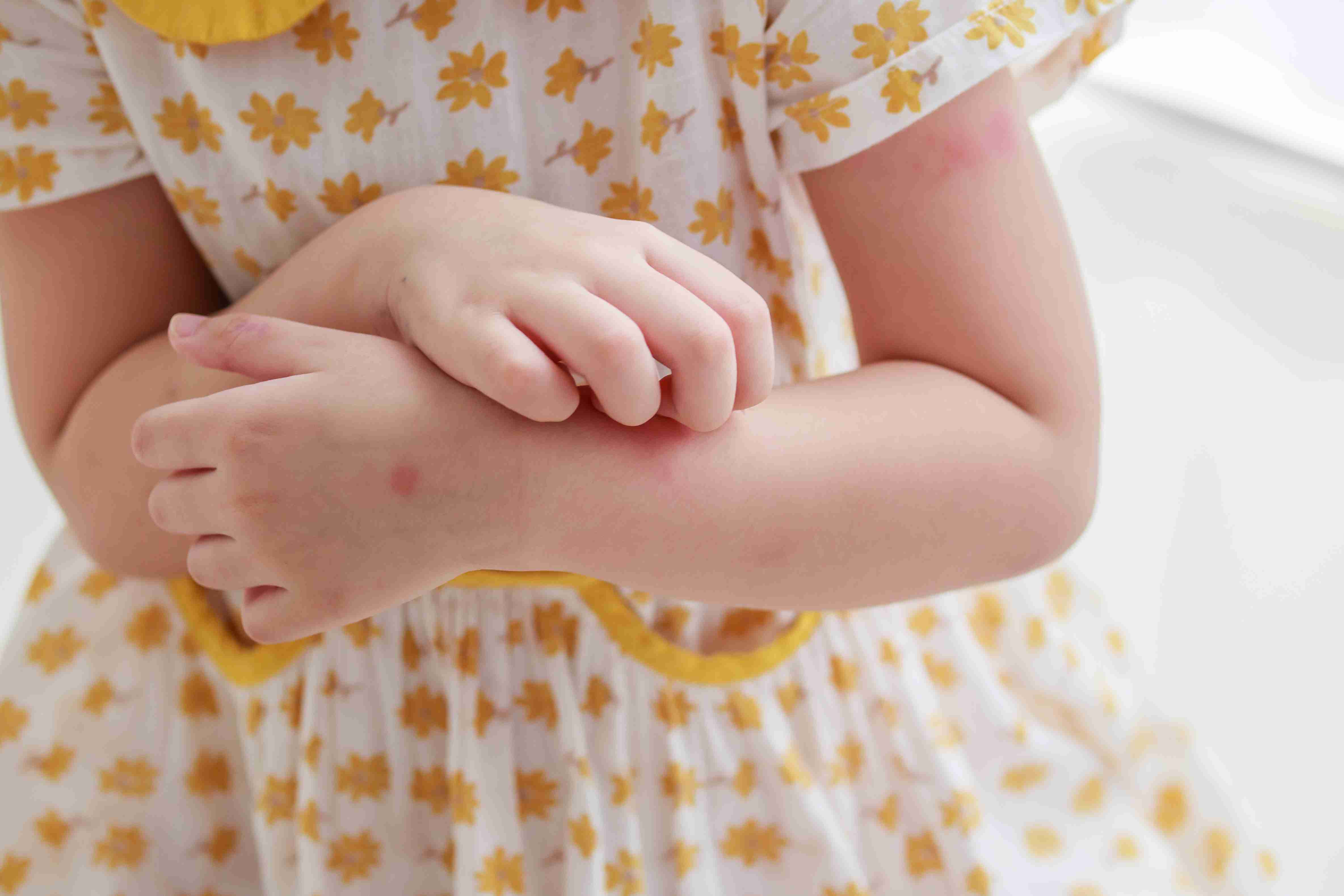

Treatment Options for Urticaria
Treatment Options for Acne
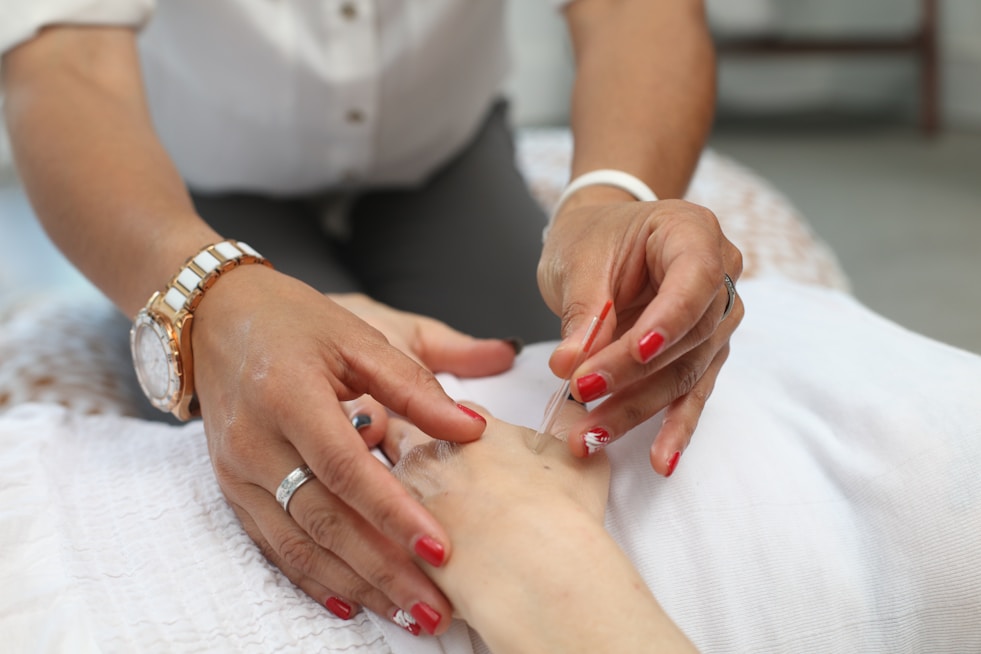

Laser Treatment
Advanced laser therapy for precise skin treatment and rejuvenation with minimal downtime and maximum results.
Chemical Peels
Professional chemical peel treatments to exfoliate and revitalize your skin for a fresh, youthful appearance.
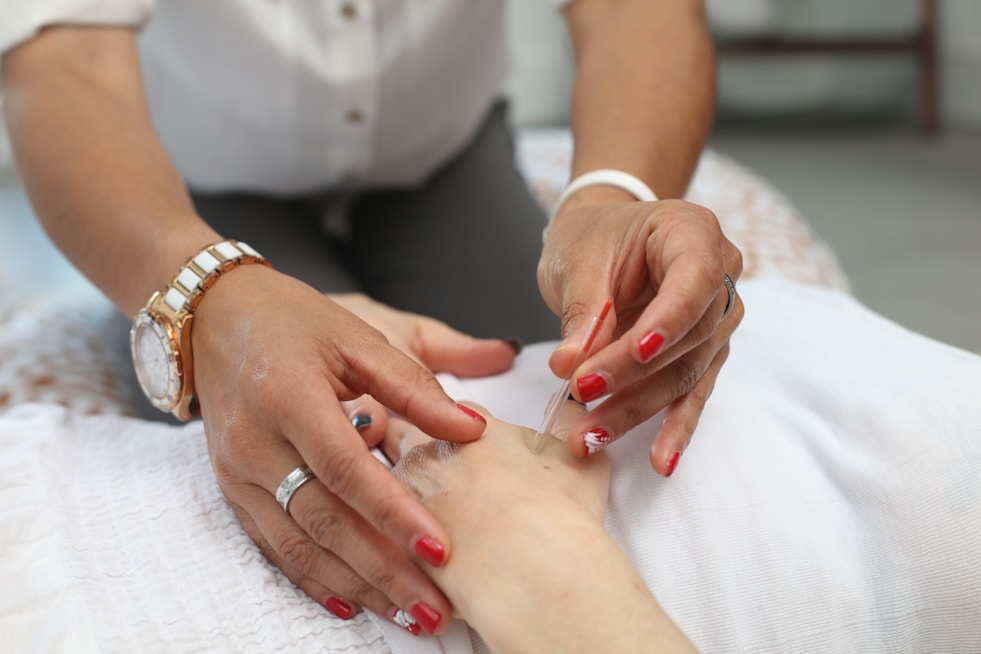

Topical Medications
Prescription-grade topical solutions customized for your specific skin condition and treatment needs.
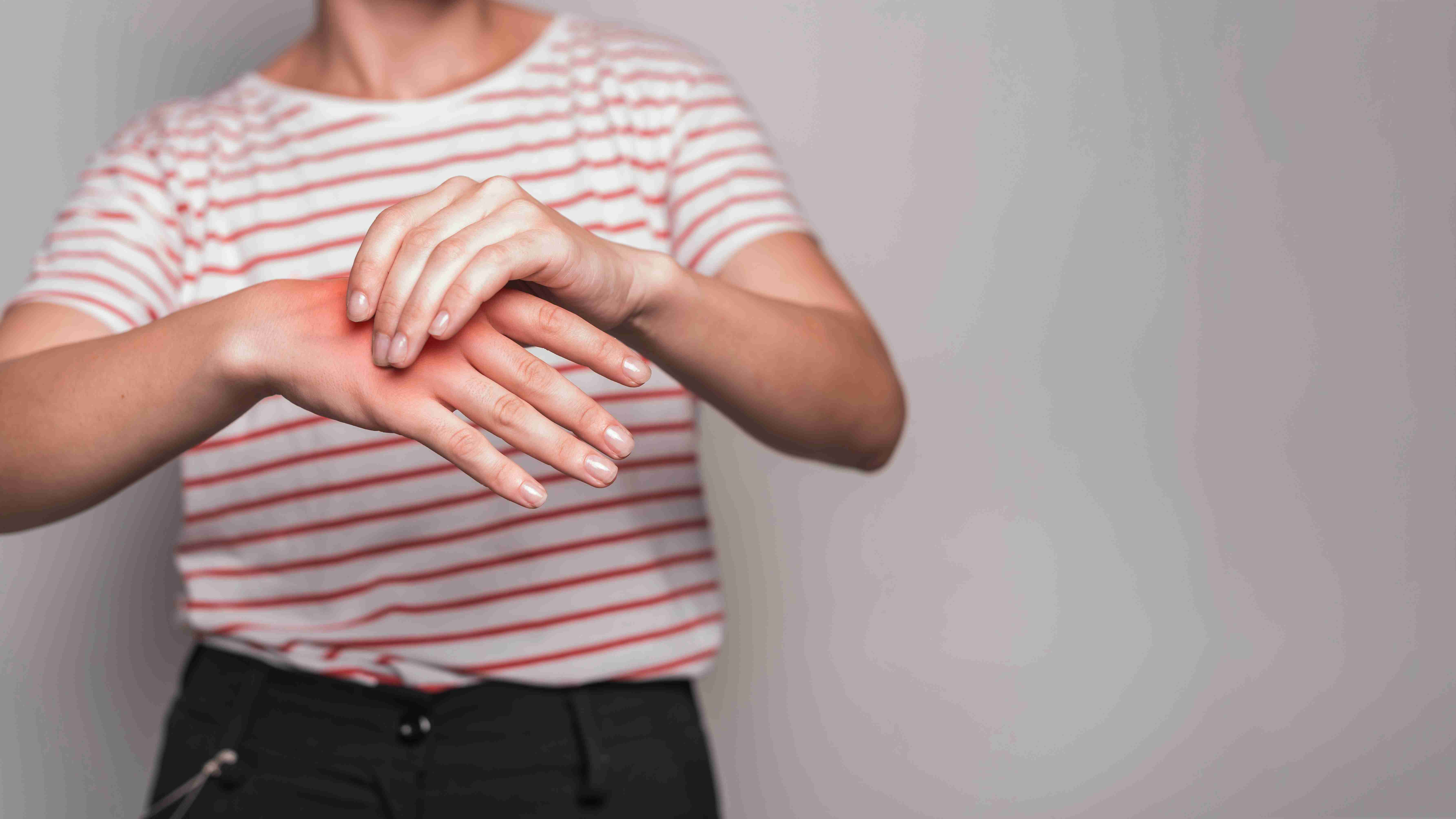

When to See a Dermatologist
If hives persist beyond a few days, occur frequently, or interfere with sleep or daily activities, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist. Chronic urticaria or angioedema should not be self-treated.
Treatment Flow
01
Clinical Assessment
Detailed history and physical examination to identify triggers and type.
02
Medication Plan
Prescription of antihistamines or short-course steroids depending on severity.
03
Allergy Workup (if needed)
Blood tests or skin testing to identify allergens in chronic cases.
04
Follow-up & Preventive Care
Review of progress and lifestyle modifications to reduce flare-ups.
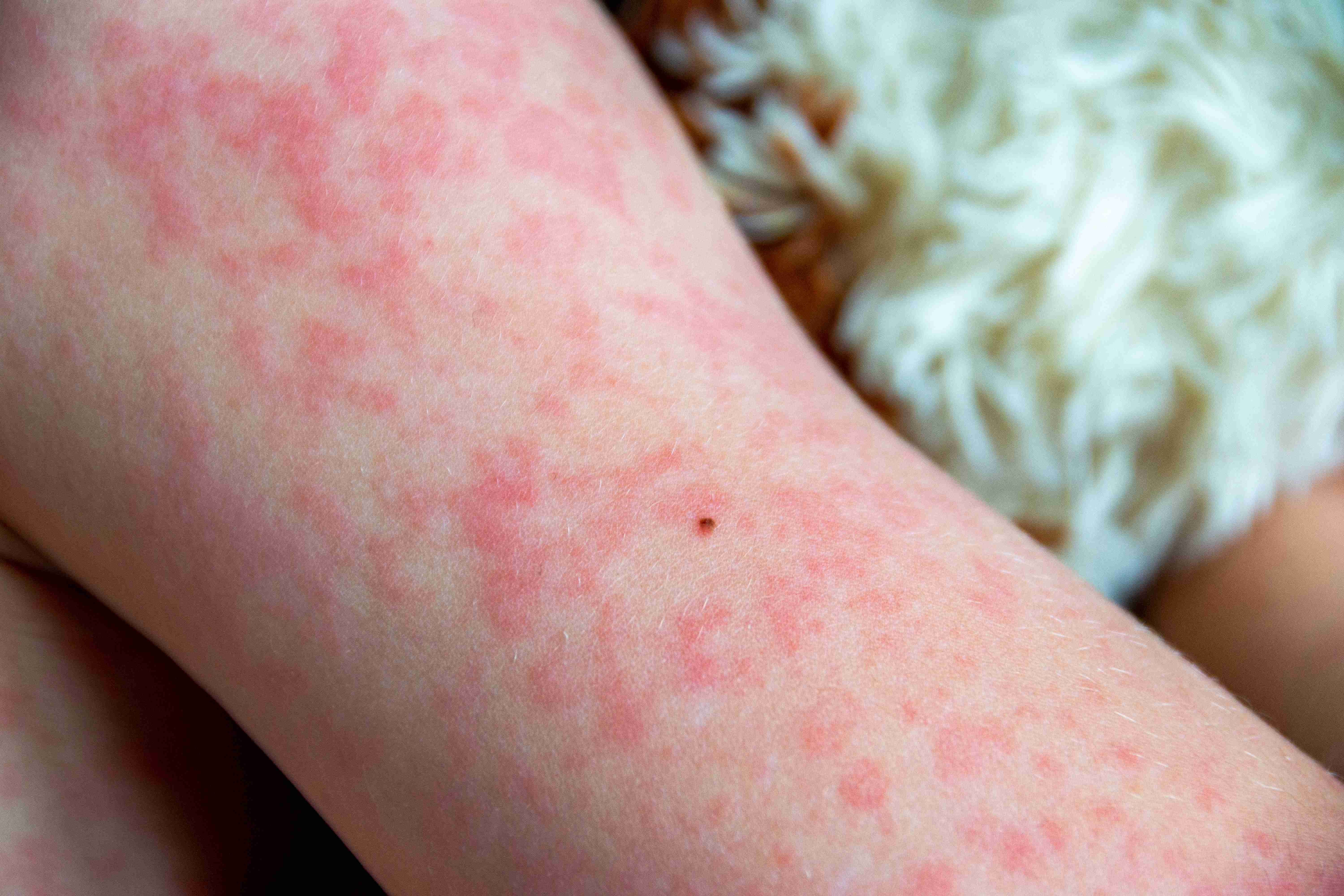
Expected Results & Relief
Symptom relief often starts within hours of antihistamine intake.
Chronic cases may take weeks for full remission but remain manageable.
Avoiding known triggers helps prevent recurrence.
Got Questions?We've Got Answers
Everything you need to know about donating, eligibility, and how The Blood App works. Can't find the answer you're looking for? Chat with our support team — we're here to help.
Most cases are harmless, but hives with lip/tongue swelling or breathing difficulty require immediate emergency care.
Yes, stress is a known trigger for both acute and chronic urticaria in many individuals.
Mild cases may resolve in a day, but chronic urticaria needs ongoing treatment.
Yes, non-sedating antihistamines can be taken regularly under dermatological supervision.
Chronic urticaria lasts more than 6 weeks, often without an identifiable allergen, and may require specialized treatment.
Start Your Personalized Skincare Plan
At ClairéDerma, we believe that healthy, radiant skinis the foundation of confidence and well-being. Ledby Dr. Mohna Chauhan, our clinic offers personalized dermatological care tailored to each patient's unique needs. With over a decade ofexperience and more than 3000 successfully treated patients,