Contact Dermatitis
Treat and Prevent Skin Reactions from Irritants and Allergens
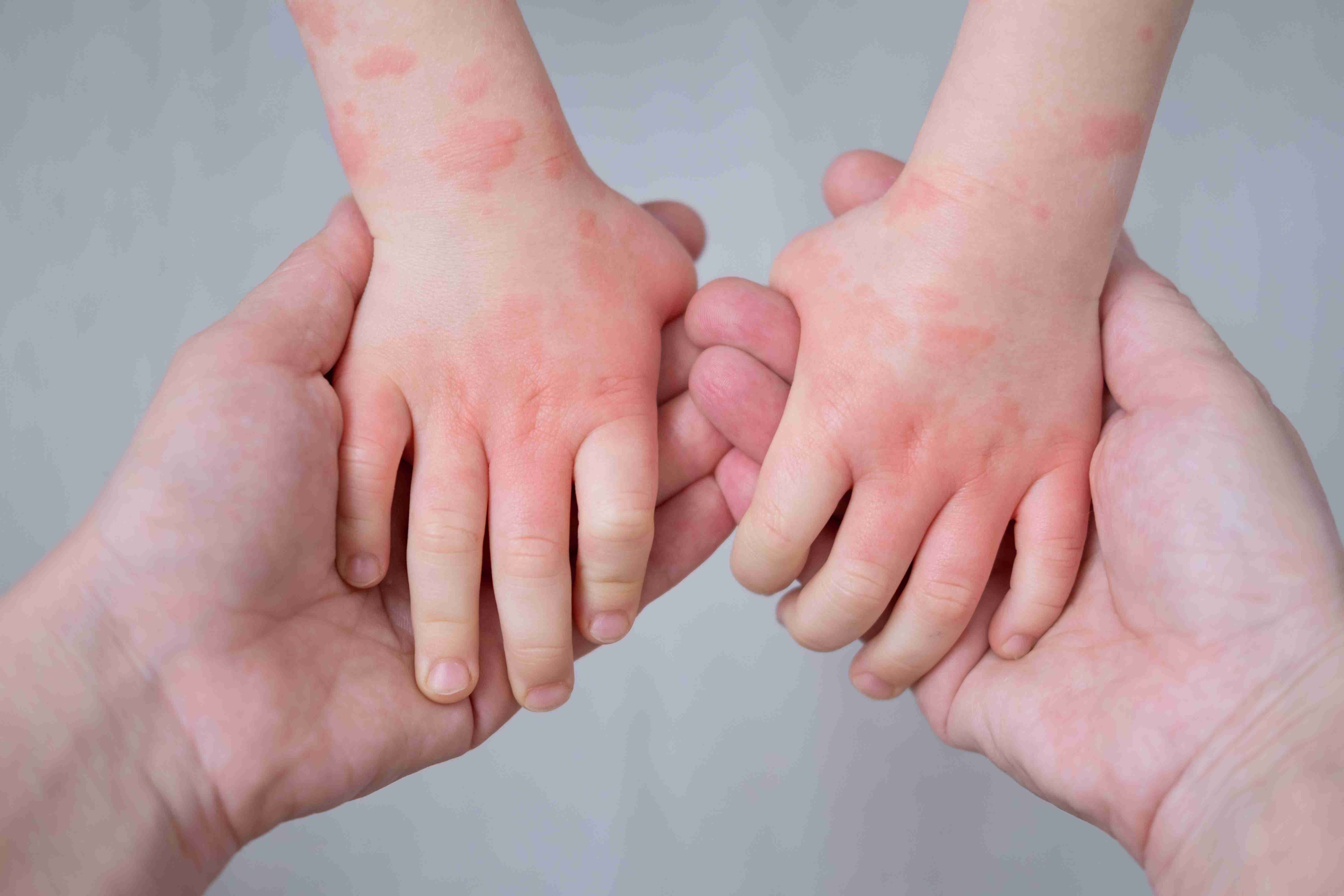

What is Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is a skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with an irritant or allergen. It typically causes red, itchy, and sometimes blistered or cracked skin. The condition can affect any part of the body but is most common on the hands, face, neck, or areas exposed to chemicals, soaps, metals, or cosmetics.
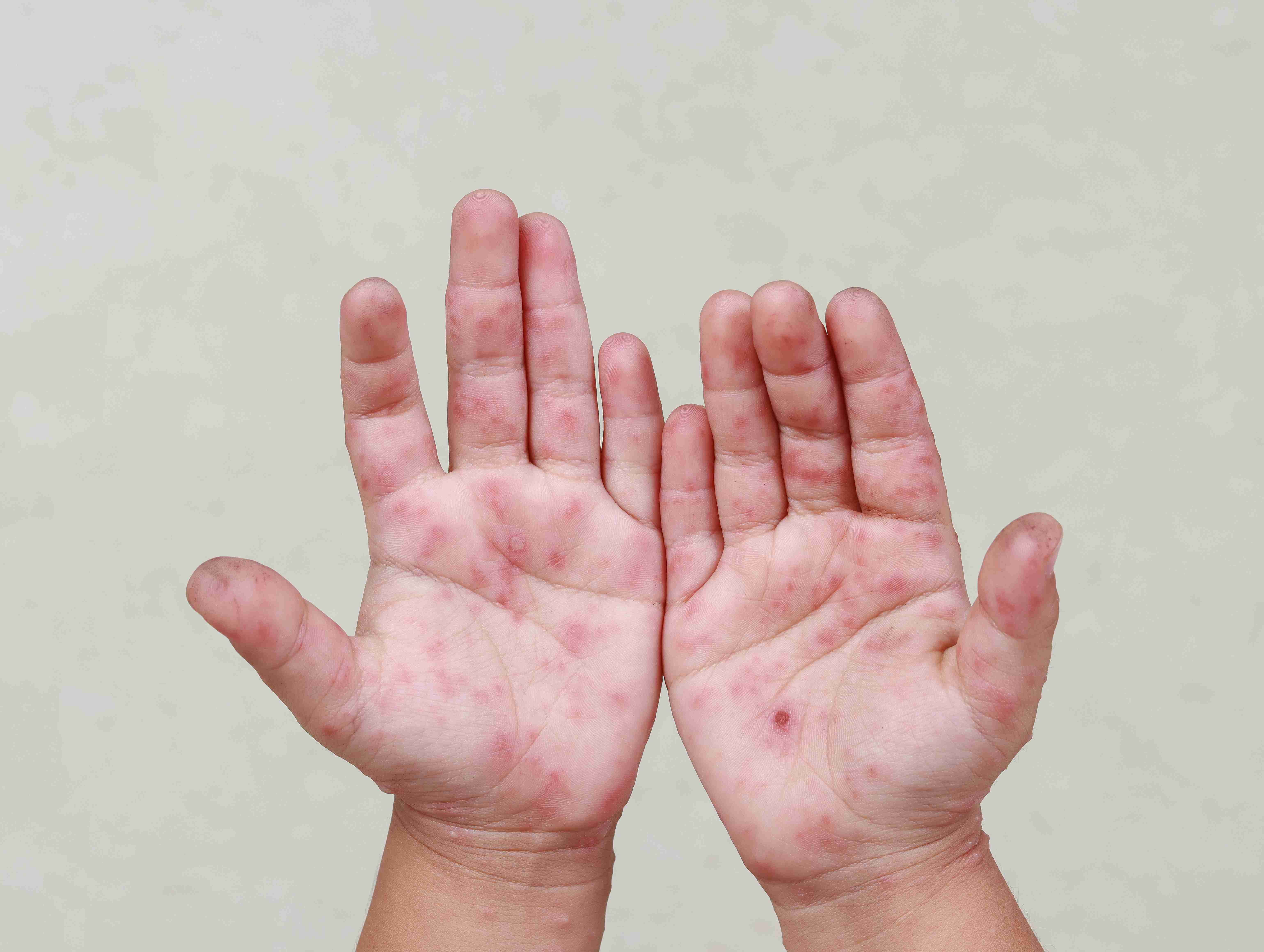
Treatment Options
Treatment Options for Acne

Laser Treatment
Advanced laser therapy for precise skin treatment and rejuvenation with minimal downtime and maximum results.
Chemical Peels
Professional chemical peel treatments to exfoliate and revitalize your skin for a fresh, youthful appearance.

Topical Medications
Prescription-grade topical solutions customized for your specific skin condition and treatment needs.
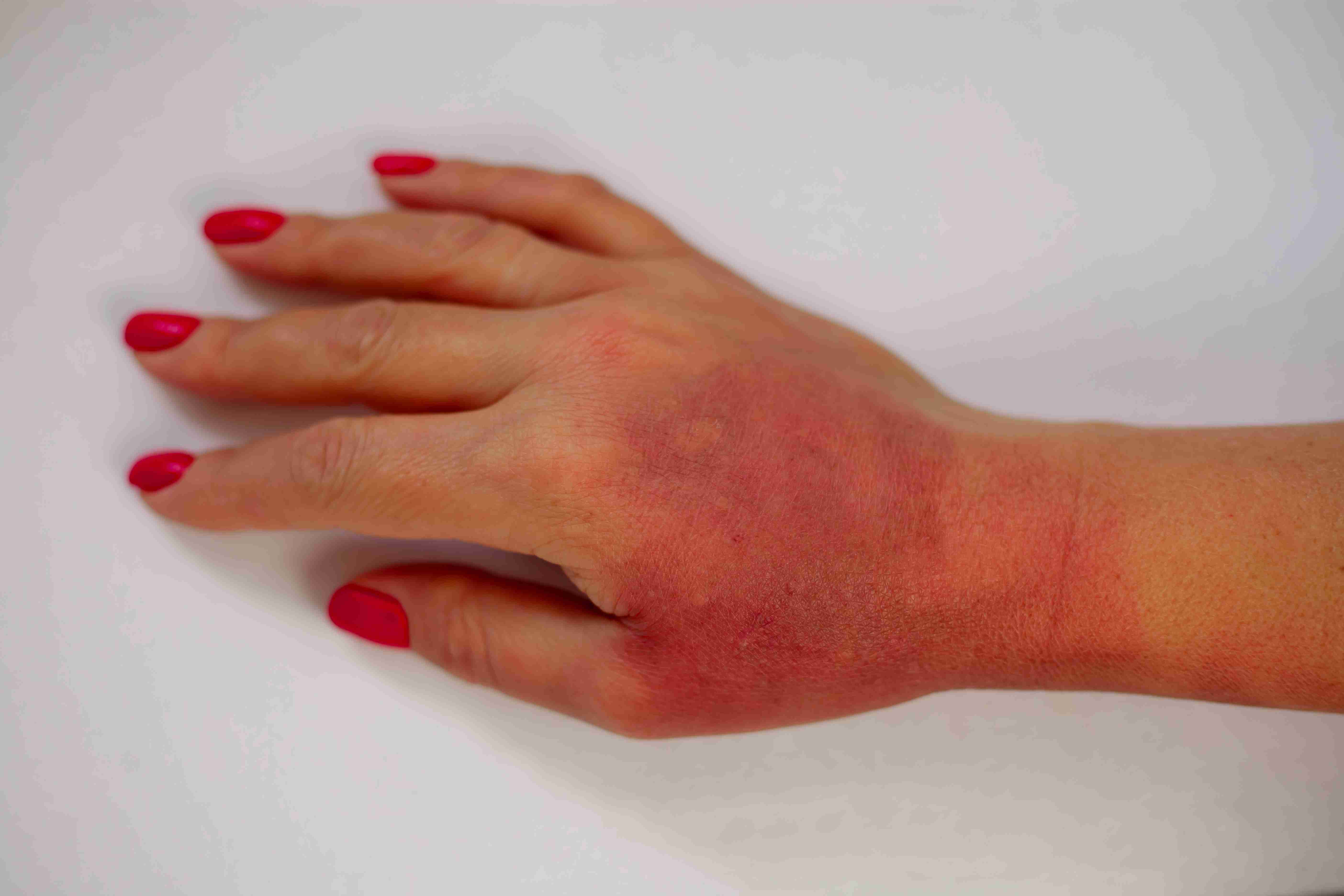
Who is Prone to Contact Dermatitis?
Individuals with sensitive skin, frequent exposure to soaps, chemicals, cosmetics, gloves, or metals (e.g., nickel) are more prone to developing contact dermatitis. Healthcare workers, beauticians, and cleaning staff are especially at risk.
Treatment Process
01
Detailed Consultation
Dermatologist assesses skin reaction and takes exposure history.
02
Trigger Identification
Patch test may be done to identify allergens if allergic dermatitis is suspected.
03
Treatment Prescription
Topical steroids, antihistamines, and barrier repair creams prescribed.
04
Education & Prevention
Advice on avoiding triggers and protecting the skin from recurrence.
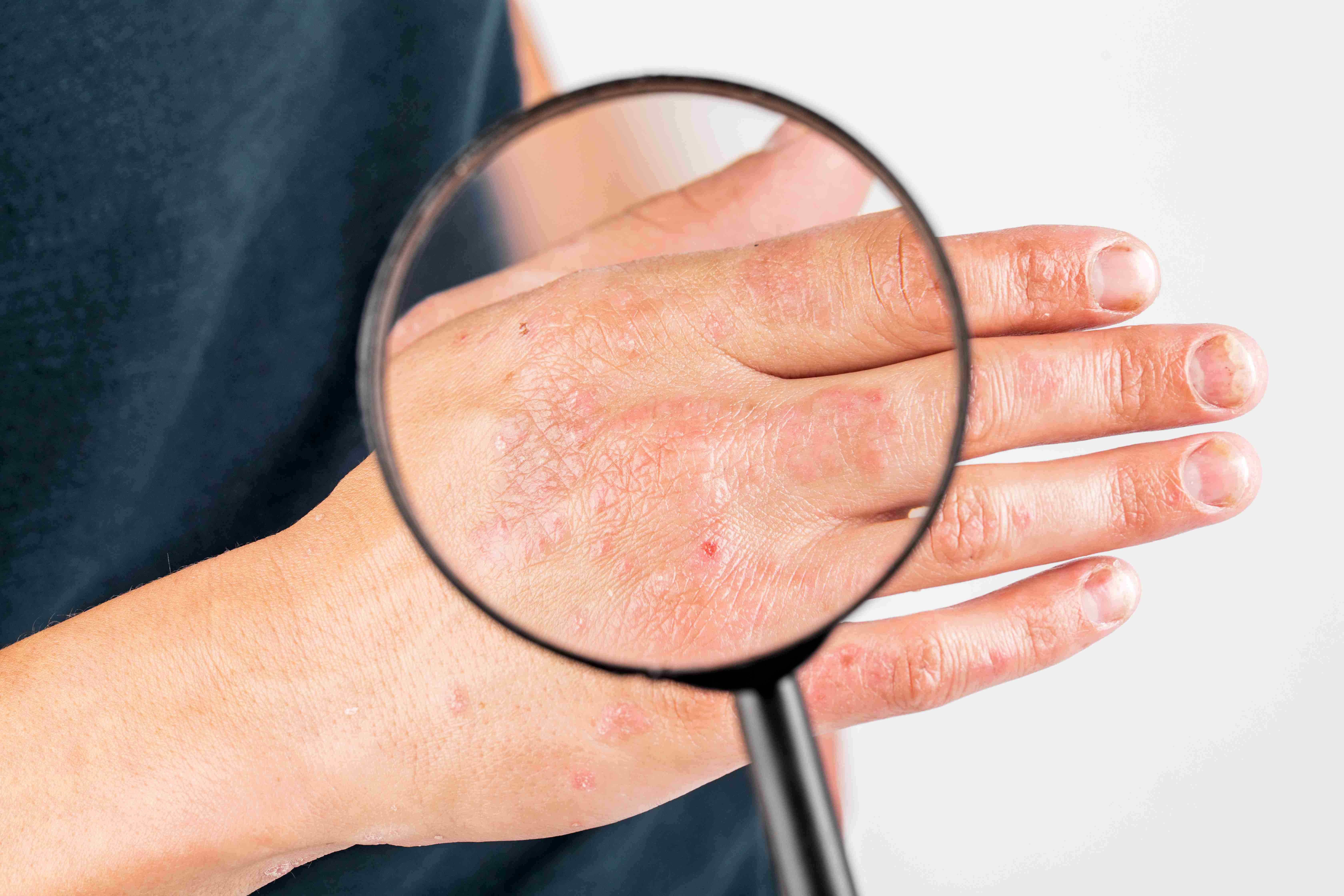
Results & Recovery
Most cases improve within 7–10 days with proper treatment.
Reduced itching and redness within 2–3 days.
Avoiding irritants helps prevent recurrence completely.
Got Questions?We've Got Answers
Everything you need to know about donating, eligibility, and how The Blood App works. Can't find the answer you're looking for? Chat with our support team — we're here to help.
No, contact dermatitis is not contagious and cannot spread from one person to another.
Mild cases may improve with moisturizers and avoiding irritants. For persistent rashes, see a dermatologist.
Patch testing helps identify allergic triggers, especially in chronic or unexplained cases.
It can, if exposure to the allergen or irritant happens again. Avoidance is key.
Contact dermatitis is a type of eczema, usually triggered by external factors. It may co-exist with other forms of dermatitis.
Start Your Personalized Skincare Plan
At ClairéDerma, we believe that healthy, radiant skinis the foundation of confidence and well-being. Ledby Dr. Mohna Chauhan, our clinic offers personalized dermatological care tailored to each patient's unique needs. With over a decade ofexperience and more than 3000 successfully treated patients,