Premature Greying of Hair
Combat Early Hair Whitening with Proven Treatments and Scalp Therapies
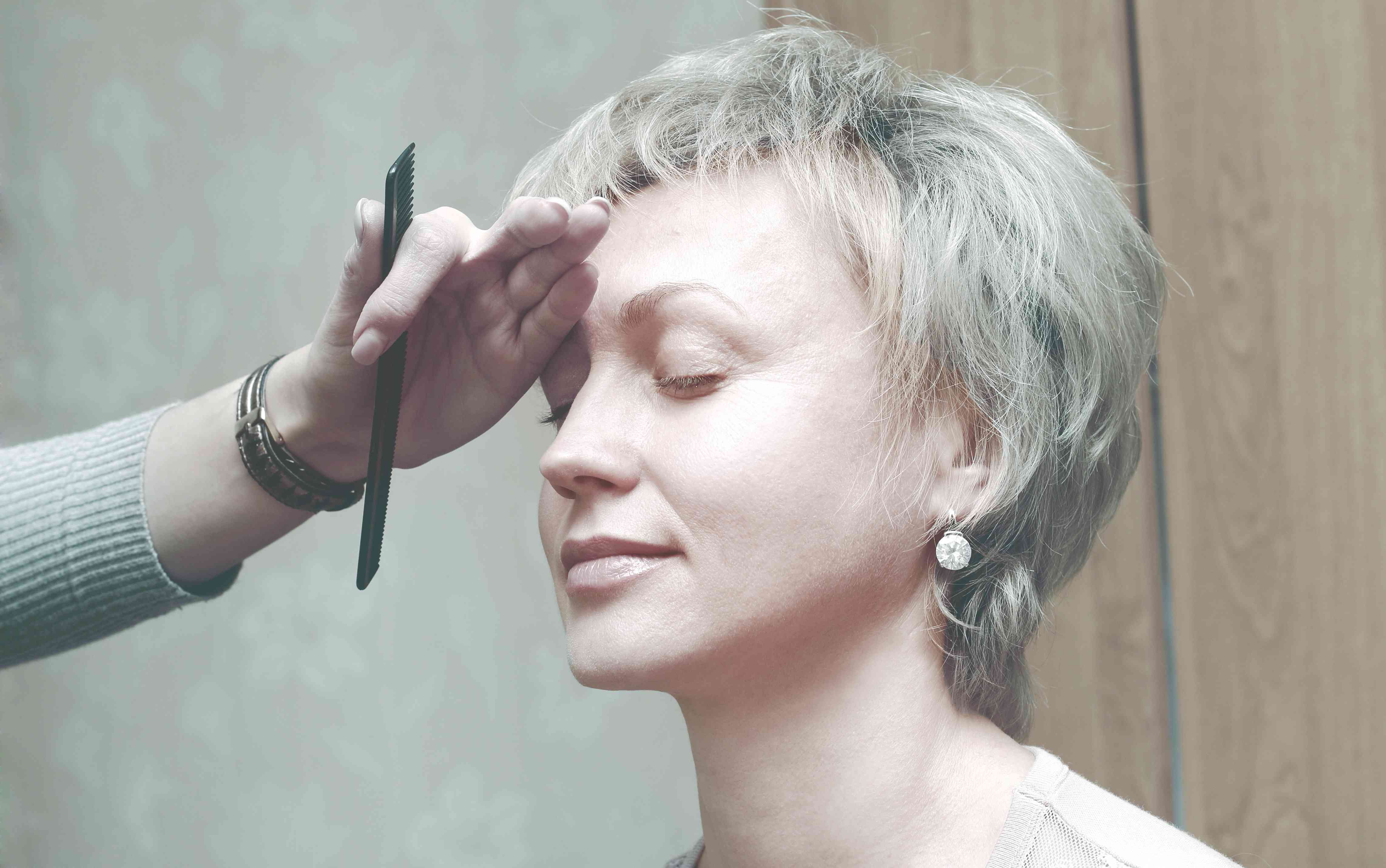

Understanding Premature Greying of Hair
Premature greying of hair refers to the early loss of natural hair color due to reduced melanin production by melanocytes. This usually occurs before the age of 30 and can significantly affect self-confidence. While genetics is the most common cause, environmental factors such as stress, nutritional deficiencies, and medical conditions may also accelerate the process.
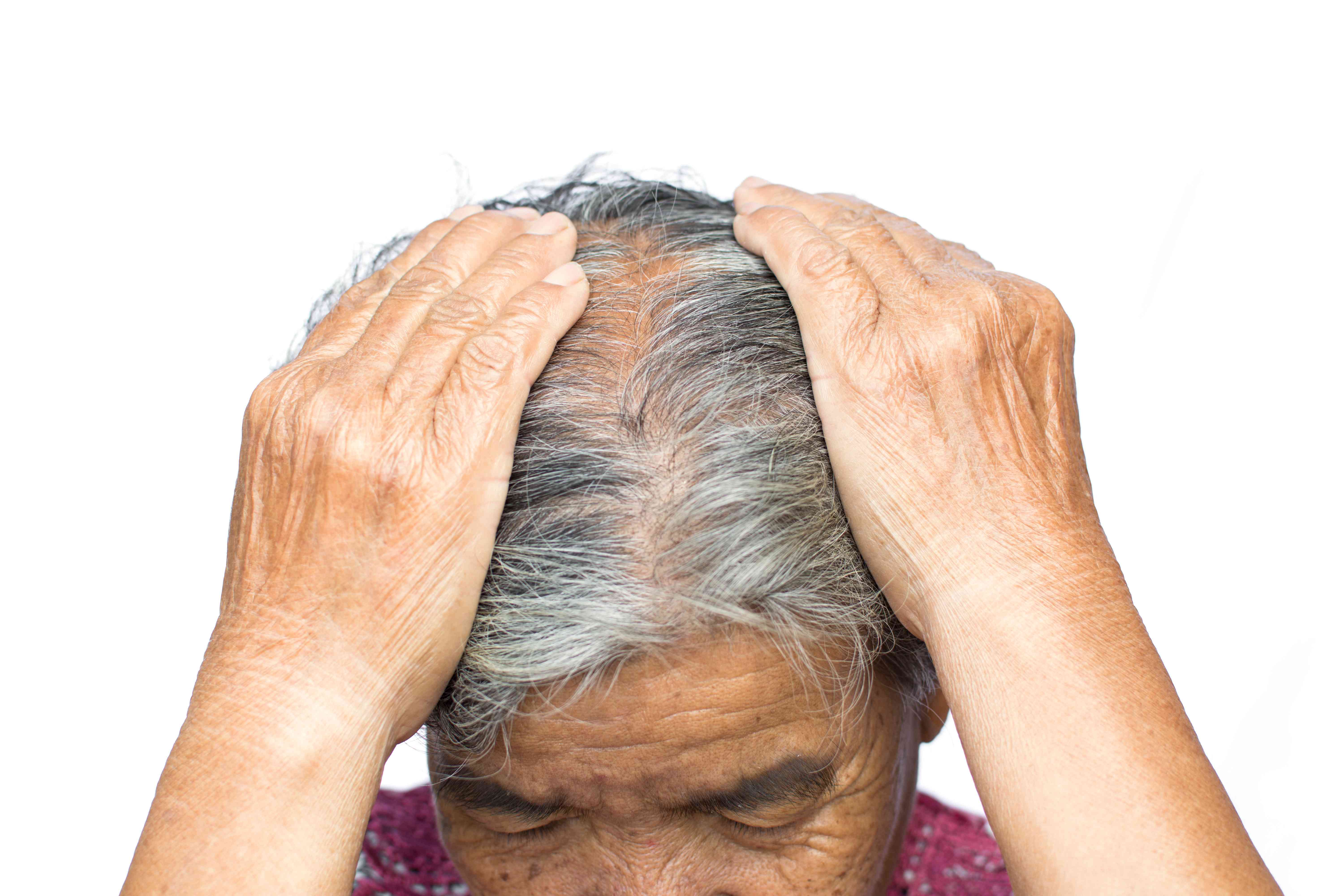

Treatment Options for Premature Greying of Hair
Treatment Options for Acne

Laser Treatment
Advanced laser therapy for precise skin treatment and rejuvenation with minimal downtime and maximum results.
Chemical Peels
Professional chemical peel treatments to exfoliate and revitalize your skin for a fresh, youthful appearance.
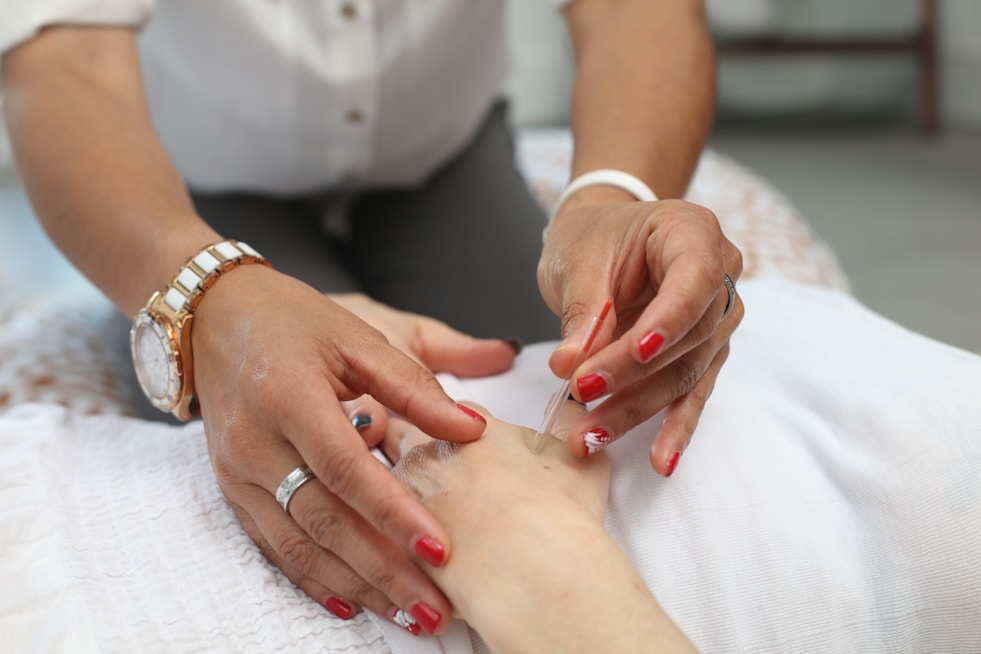

Topical Medications
Prescription-grade topical solutions customized for your specific skin condition and treatment needs.
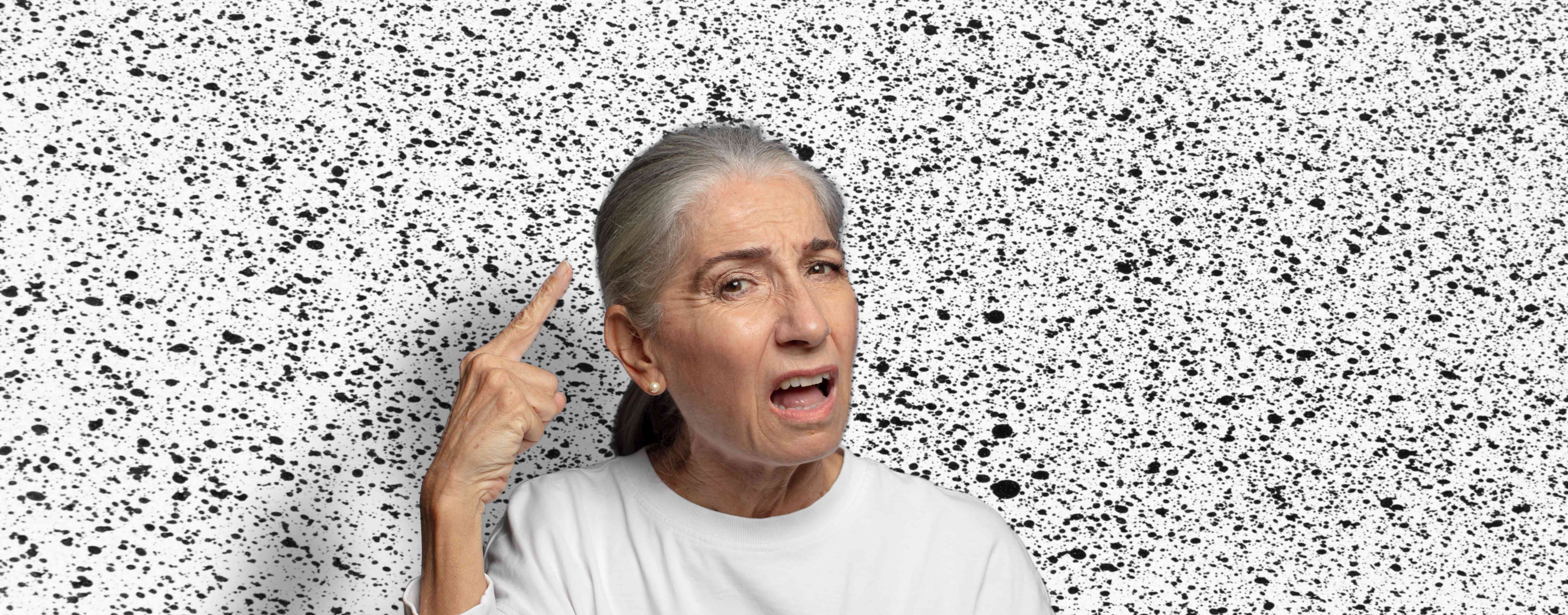

Who Can Benefit from Treatment?
Anyone experiencing premature greying in their teens, 20s, or early 30s can benefit from timely treatment. Whether due to genetics, lifestyle, or deficiencies, expert intervention can slow the progression and improve hair health. Suitable for both men and women.
Treatment Journey
01
Diagnosis & Assessment
A complete evaluation of scalp health, vitamin levels, and medical history is conducted.
02
Therapeutic Intervention
Personalized plans including serums, supplements, and therapies are prescribed to address root causes.
03
Ongoing Support
Regular follow-ups with adjustments to treatment and lifestyle recommendations to maintain outcomes.
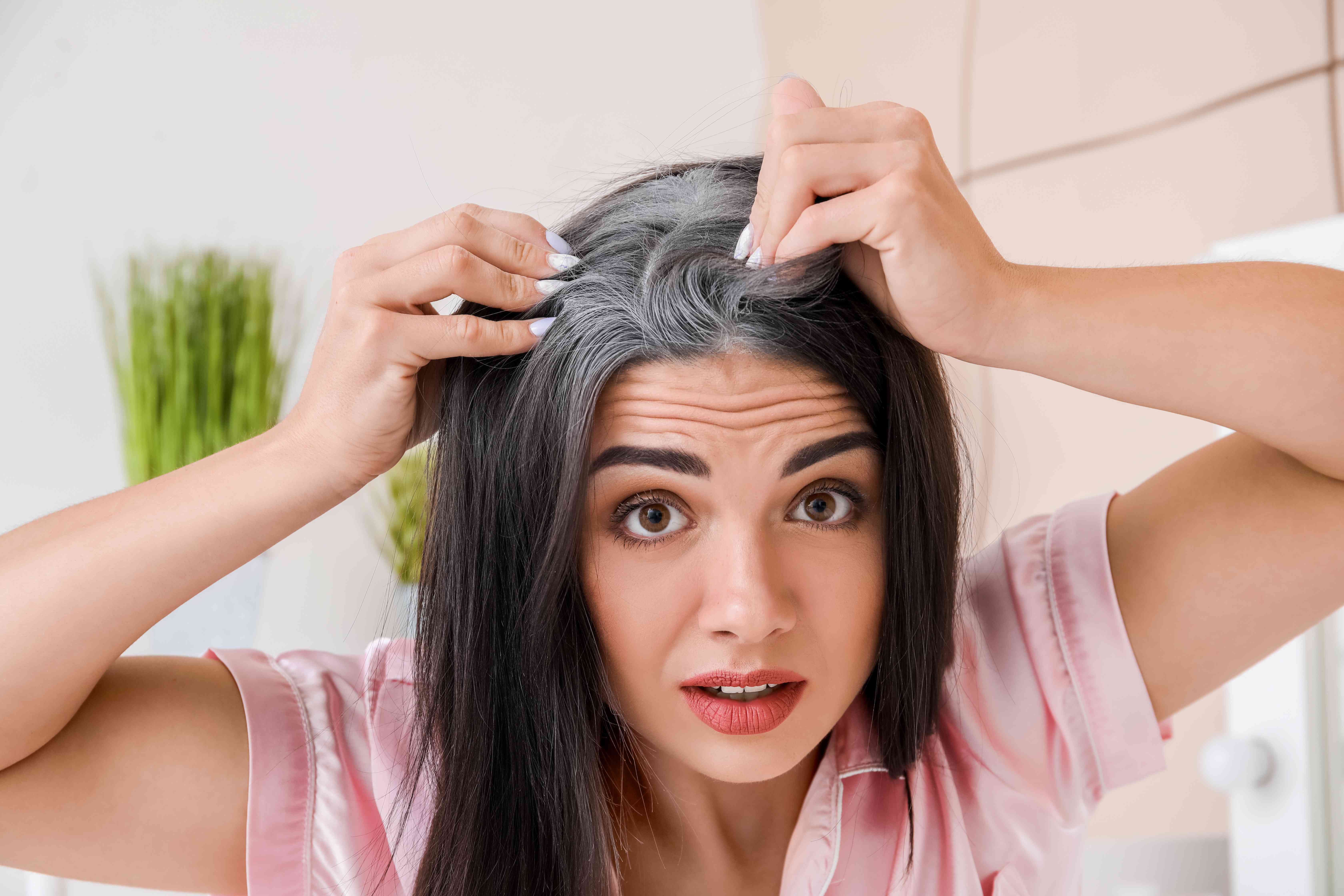

Expected Results
Noticeable slowing of greying process over consistent treatment cycles.
Healthier, shinier, and stronger hair overall.
Reduced reliance on hair dyes and improved confidence.
Got Questions?We've Got Answers
Everything you need to know about donating, eligibility, and how The Blood App works. Can't find the answer you're looking for? Chat with our support team — we're here to help.
It can often be slowed or partially reversed if treatment begins early and underlying causes are addressed.
In Indian populations, greying before 25 is typically considered premature.
Yes, high stress levels and poor sleep can accelerate follicle aging and pigment loss.
If the greying is due to nutritional deficiencies, supplements can be very effective when used correctly.
Yes, dermatologically approved ammonia-free hair colors are safe to use during treatment.
Start Your Personalized Skincare Plan
At ClairéDerma, we believe that healthy, radiant skinis the foundation of confidence and well-being. Ledby Dr. Mohna Chauhan, our clinic offers personalized dermatological care tailored to each patient's unique needs. With over a decade ofexperience and more than 3000 successfully treated patients,